Explanation Needed: Understanding CMOS in Computers
The fundamental part of a computer's motherboard is the CMOS, an acronym for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor. The component plays a critical role in system configuration and timekeeping. While often overlooked by casual computer users, CMOS is essential for maintaining crucial system settings and ensuring proper system functionality.
First, what is a CMOS
The CMOS is referred to as a small amount of non-volatile memory that stores BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) settings on a computer. These particular settings include system time, date, and hardware configurations such as boot order, processor settings, and memory timings. Unlike conventional RAM, COMOS requires a constant power source to remain functional, typically provided by a small battery, to retain data when the computer is powered down.
Understanding the Difference between CMOS vs. BIOS
Often mentioned together, the CMOS and BIOS serve different functions. The BIOS is a firmware stored in a chip on the motherboard that facilitates hardware initialization and system startup procedures. On the other hand, the CMOS holds settings that the BIOS references when configuring hardware during the bootup process. When users need to adjust the settings in the BIOS menu, those changes are stored in the CMOS.
What you see right there in this image is an actual CMOS battery on a motherboard
The actual Role of the CMOS
As we discussed in the paragraph above, CMOS requires continuous power from a small, coin-sized battery — often a CR2032 — embedded in the motherboard to maintain stored settings even when the PC is powered down. If the battery fails, the CMOS resets, causing the system to lose stored configurations such as time settings and custom boot preferences, which must then be reconfigured manually upon startup.
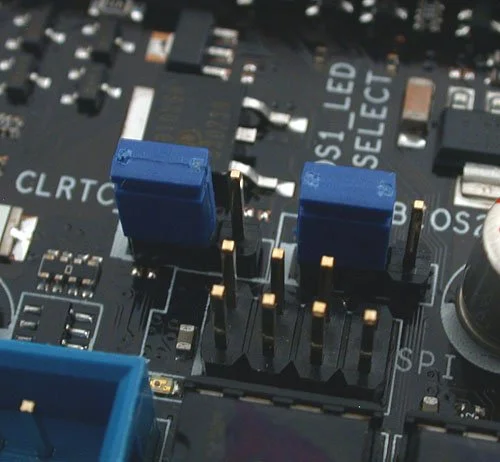
This is an image of blue jumper caps on jumpers.
PC Troubleshooting and CMOS Reset
There are times when users may need to reset the CMOS due to system errors, failed overclocking attempts, or hardware compatibility issues. Resetting is made possible by either removing the CMOS battery for a few minutes or using the motherboard’s jumpers, which are explicitly designed for reset functions. Resetting CMOS restores BIOS settings to factory default state, potentially resolving computer issues or hardware conflicts.
The Modern CMOS in Computers
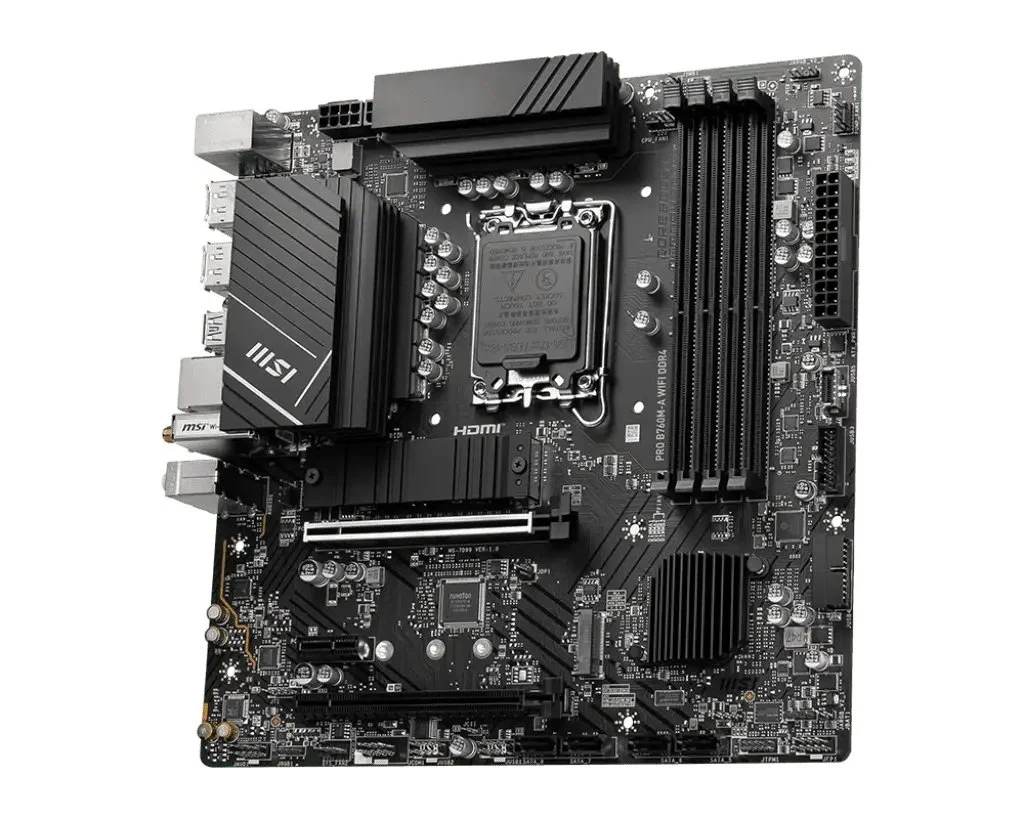
While the traditional CMOS-based configurations remain relevant today, modern systems are increasingly replacing CMOS memory with flash storage, which does not require a battery to retain information. This technological shift enhances reliability and reduces the need for manual reset caused by battery failure.
This is a modern motherboard that does not have a CMOS battery
Conclusion
The CMOS is a small yet crucial component that ensures the stability of system settings. Its function in maintaining BIOS configurations and hardware preferences allows computers to boot correctly and retain essential data. Understanding CMOS can be beneficial for troubleshooting and optimizing a computer's performance, making it a necessary aspect of motherboard architecture.