Explanation Needed: What is The CPU socket and How Dose it Function?
When upgrading or building a PC, we often overlook the CPU socket, despite its importance. How important is this component, you ask? It's where you insert the processor. Unlike other components on the motherboard, the CPU socket plays a vital role in your PC's performance. Without it, the processor would be a useless piece of hardware.
First, the Basics
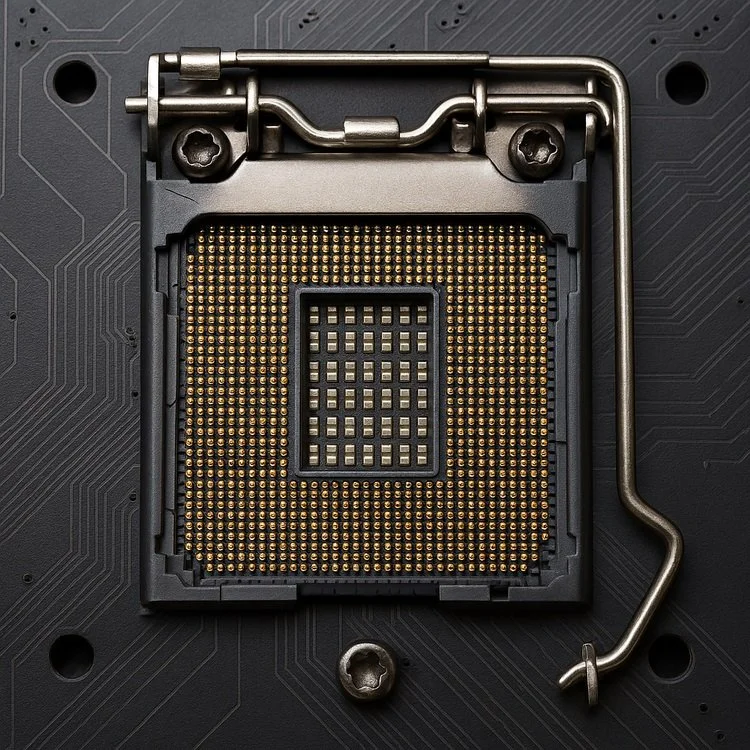
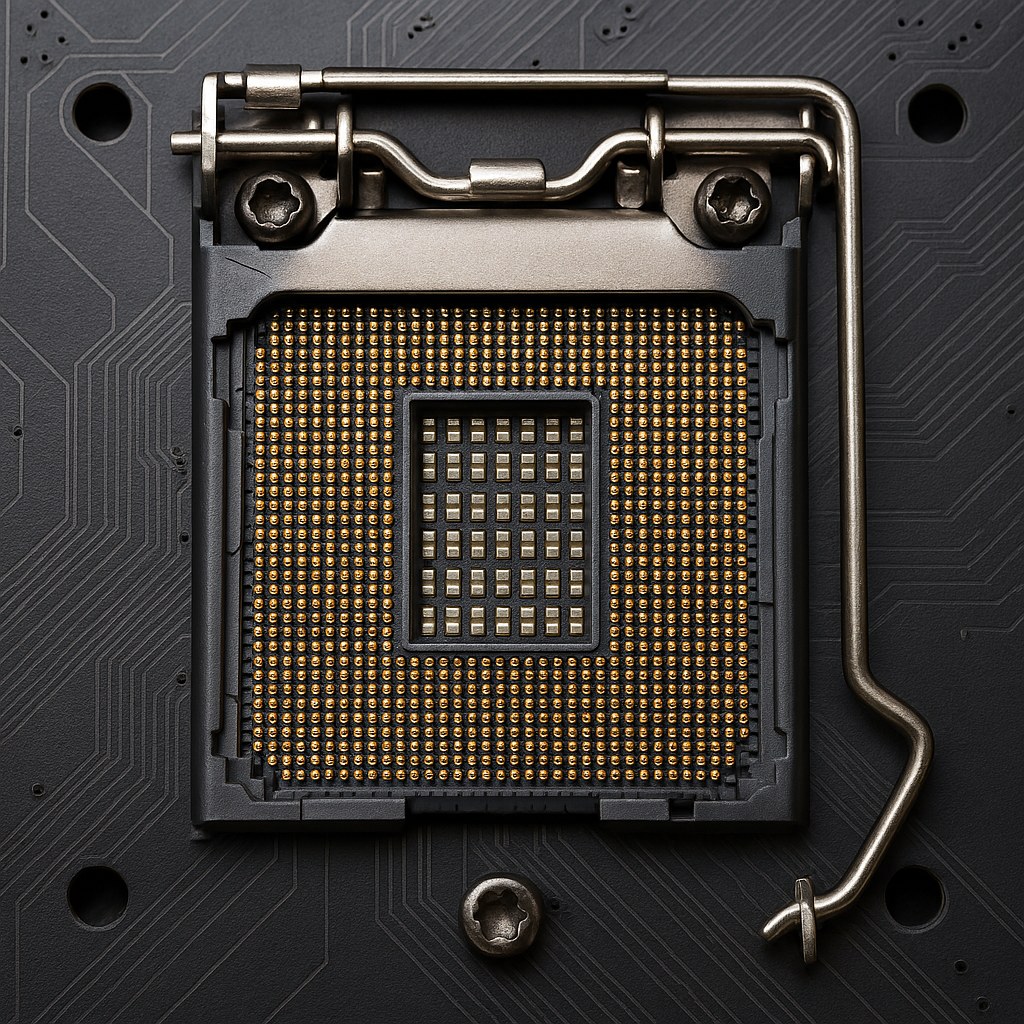
The CPU socket is a physical interface located on the motherboard that connects the CPU to the rest of the system. It provides both mechanical support and electrical connectivity, allowing for the CPU to communicate with other components, including memory, Storage, and peripherals, while receiving power.
Unlike some systems with soldered CPUs found in laptops, desktop CPU sockets have a modular design for intuitive hardware installation. Making it essential for PC enthusiasts and gamers alike who want flexibility and upgradability.
The Types of CPU Sockets
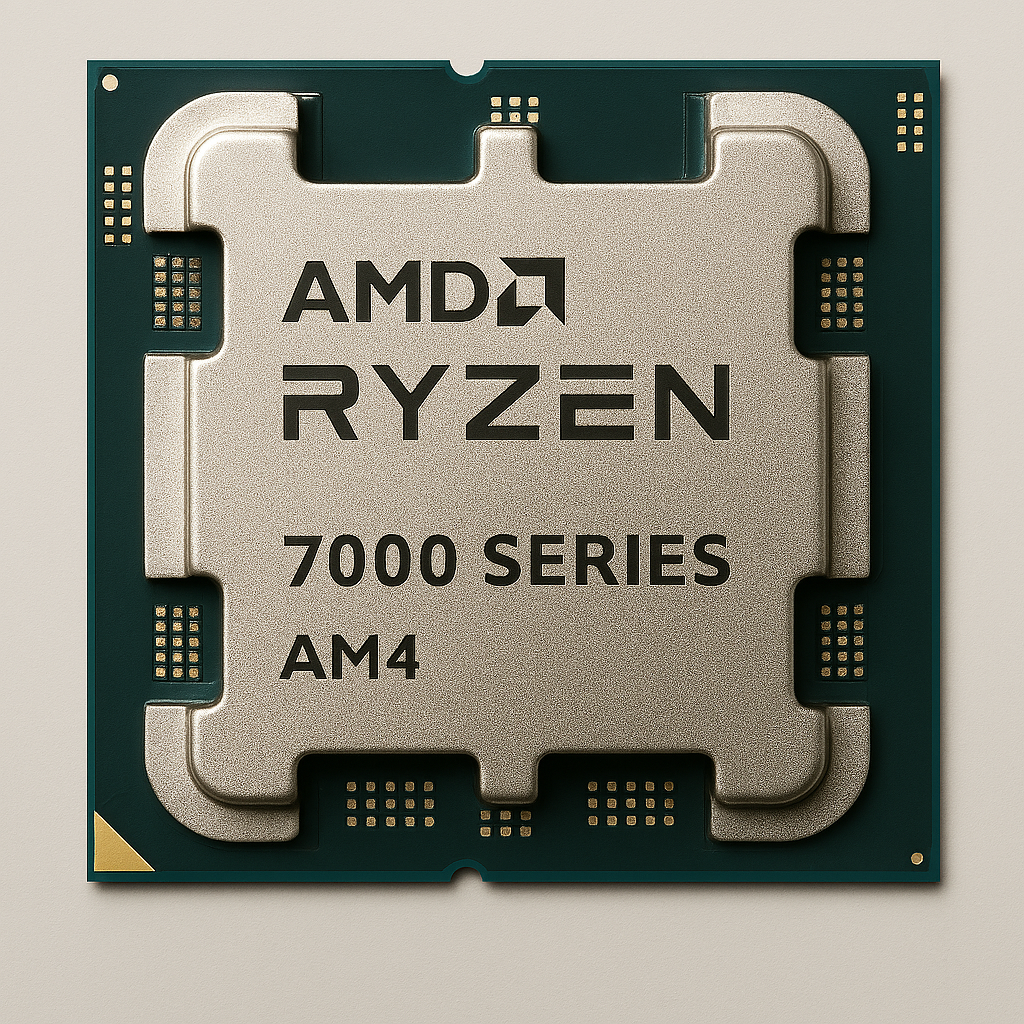
There are several types of CPU socket designs, each with its own unique layout and pin configuration. Firstly, you have the Land Grid Array (LGA). The Intel-based socket pins are located on the motherboard, with the CPU featuring flat contact pads. The PGA ( Pin Grid Array) used by AMD has pins directly on the CPU, with the socket having Holes. Finally, the Ball Grid Array (BGA) CPU is soldered directly to the board. This particular socket is found in laptops and systems with embedded hardware.
Most modern desktop systems' CPUs today use either LGA or PGA sockets, with LGA being the dominant socket of Intel's lineup and PGA being common in AMD’s mainstream offerings.
What Does it All Mean?
Choosing the right CPU socket isn't just about the CPU's physical fit; it's about compatibility. Each CPU socket type supports a specific type of processor series and chipset. Here's an example :
Intel's LGA 1700 supports 12th and 13th-generation Core processors.
AMD's AM4 socket supports Ryzen series 5000, 7000, and 9000 processors.
It is quite possible to install the processor into the socket incorrectly, which can cause severe damage to both the CPU and the motherboard.
Install With Care
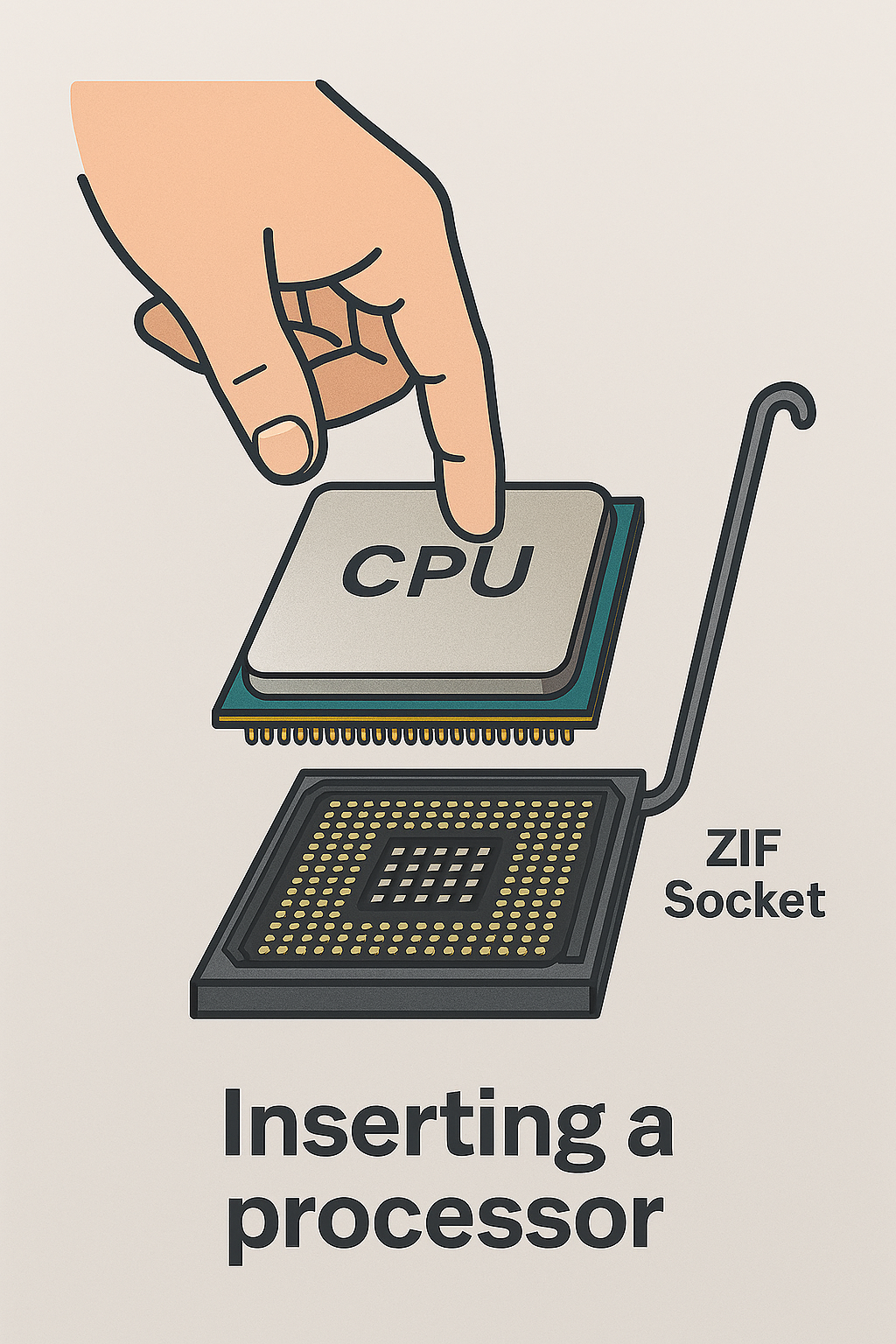
Most CPU sockets feature a Zero Insertion Force ( ZIF in short) mechanism, which allows the CPU to be placed gently into the socket ( keyword: Gently) and locked in with a lever or latch--reducing the risk of bending and damage to the contact pins.
Here is a list of recommendations on how to carefully insert the processor into a socket:
-Always align the CPU correctly using the physical indicators or triangle markers. If you pay close attention to the etched marker, it should be impossible to install the processor incorrectly.
-Avoid touching the contact pads or pins
-Use an anti-static wrist strap or ground yourself by touching a metallic object.
The Longevity Advantages
One of the most significant advantages of socketed CPUs is the user’s ability to upgrade. As long as the motherboard supports the newer processor (through the BIOS or chipset compatibility), users can swap out CPUs without replacing the entire motherboard.
However, socket standards evolve throughout time, and Intel and AMD periodically release new socket designs to support advancements in power delivery, memory bandwidth, and thermal management.
My Final Thoughts
For many, the CPU socket may not be the attractive star of your PC build, but it sets the stage for the processor’s performance. Understanding the role of the CPU socket will help you make more informed decisions when choosing hardware for future builds or planned upgrades.